简体中文
繁體中文
English
Pусский
日本語
ภาษาไทย
Tiếng Việt
Bahasa Indonesia
Español
हिन्दी
Filippiiniläinen
Français
Deutsch
Português
Türkçe
한국어
العربية
The CPI and Forex: How CPI Data Affects Currency Prices
Abstract:In this article, we’ll explore CPI and forex trading, looking at what traders should know about the Consumer Price Index to make informed decisions. We’ll cover what CPI is as a concept, the CPI release dates, how to interpret CPI, and what to consider when trading forex against CPI data.
WHAT IS CPI AND WHY DOES IT MATTER TO FOREX TRADERS?
The Consumer Price Index, better known by the acronym CPI, is an important economic indicator released on a regular basis by major economies to give a timely glimpse into current growth and inflation levels.
Inflation tracked through CPI looks specifically at purchasing power and the rise of prices of goods and services in an economy, which can be used to influence a nations monetary policy.
CPI is calculated by averaging price changes for each item in a predetermined basket of consumer goods, including food, energy, and also services such as medical care.
It is a useful indicator for forex traders due to its aforementioned effect on monetary policy and, in turn, interest rates, which have a direct impact on currency strength. The full utility of knowing how to interpret CPI as a forex trader will be explored below.
CPI RELEASE DATES
CPI release dates usually occur every month, but in some countries, such as New Zealand and Australia, quarterly. Some nations also offer yearly results, such as Germanys index. The US Bureau of Labor Statistics has reported the CPI monthly since 1913.
The following table shows a selection of major economies and information about their CPI releases.
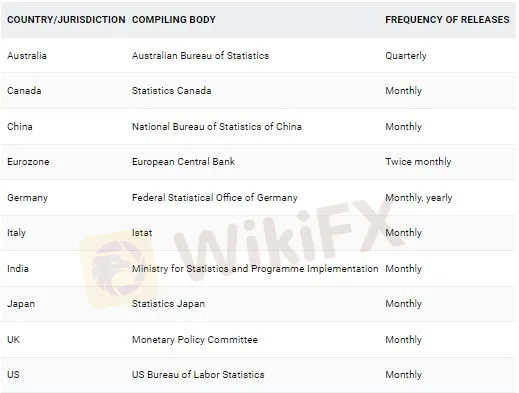
WHY FOREX TRADERS SHOULD FOLLOW CPI DATA
Understanding CPI data is important to forex traders because it is a strong measure of inflation, which in turn has a significant influence on central bank monetary policy.
So how does CPI affect the economy? Often, higher inflation will translate to higher benchmark interest rates being set by policymakers, to help dampen the economy and subdue the inflationary trend. In turn, the higher a countrys interest rate, the more likely its currency will strengthen. Conversely, countries with lower interest rates often mean weaker currencies.
The release and revision of CPI figures can produce swings in a currencys value against other currencies, meaning potentially favorable volatility from which skilled traders can benefit.
Also, CPI data is often recognized as a useful gauge of the effectiveness of the economic policy of governments in response to the condition of their domestic economy, a factor that forex traders can consider when assessing the likelihood of currency movements.
The CPI can also be used in conjunction with other indicators, such as the Producer Price Index, for forex traders to get a clearer picture of inflationary pressures.
WHAT TO CONSIDER WHEN TRADING FOREX AGAINST CPI DATA
When using CPI data to influence forex trading decisions, traders should consider the market expectations for inflation and what is likely to happen to the currency if these expectations are met, or if they are missed.
Similar to any major release, it may be beneficial to avoid having an open position immediately before. Traders might consider waiting for several minutes after the release before looking for possible trades, since forex spreads could widen significantly right before and after the report.
Below is a chart displaying the monthly inflation rates for the US. For the latest month, expectations are set at 1.6% inflation compared to last years data. If CPI is released higher or lower than expectations this news event does have the ability to influence the market.
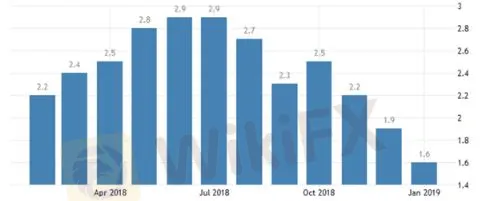
Chart to show US inflation levels in 2018/19. Source: TradingEconomics.com. US Bureau of Labor Statistics
One way the effects of CPI data can be interpreted is by monitoring the US Dollar Index, a 2018/19 example chart for which is below. If CPI is released away from expectations, it is reasonable to believe this may be the catalyst to drive the Index to fresh highs, or to rebound from resistance.
Since the Index is comprised of EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and GBP/USD, by watching the US Dollar we can get a full interpretation of the events outcome.
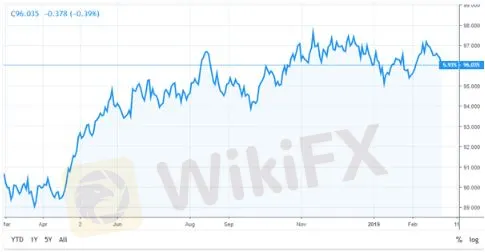
Chart to show movement in the US Dollar Index. Source: TradingView.com
As can be observed in the example above, as inflation rose during the first half of 2018, the US Dollar Index went up accordingly. But with US inflation drifting lower in the following months and with a missed target of 2%, this pushed US interest rate hikes off the agenda. As a result, the dollar struggled and weakened against a basket of other currencies.
Not every fundamental news release works out through price as expected.
Once the CPI data has been released and analyzed, traders should then look to see if the market price is moving through or rebounding off any areas of technical importance. This will help traders understand the short-term strength of the move and/or the strength of technical support or resistance levels, and help them make more informed trading decisions.
Disclaimer:
The views in this article only represent the author's personal views, and do not constitute investment advice on this platform. This platform does not guarantee the accuracy, completeness and timeliness of the information in the article, and will not be liable for any loss caused by the use of or reliance on the information in the article.
Read more

Should You Beware of Forex Trading Gurus?
Know the reality behind forex trading gurus, examining their deceptive tactics, inflated promises, and the risks associated with trusting them for financial advice.

Why More People Are Trading Online Today?
Discover why online trading is booming with tech, AI, and a push for financial freedom. From stocks to crypto, it’s a thrilling hustle for all.

High Return Traps? WikiFX’s Complete Scam-Busting Handbook to Avoid Financial Fraud!
Financial scams are evolving faster than ever, and fraudsters are getting more creative in luring victims into traps. Whether it’s promising high returns or leveraging authority to build trust, scammers continuously innovate new ways to trick investors. From clone firms to cold calling schemes, it’s essential to understand how these scams work to protect your hard-earned money. This comprehensive guide by WikiFX will help you recognize and avoid common financial scams.

Forex Explained in 60 Seconds: How It Works & Who Profits
Before diving into the forex market, it’s crucial to understand its mechanics, risks, and profit potential. Without a clear grasp of how forex operates, you risk losing money instead of making it. Here’s a concise breakdown to help you navigate this dynamic financial market.
WikiFX Broker
Latest News
The Withdrawal Trap: How Scam Brokers Lure Victims into Paying More
FCA to Investors: Think Twice Before Trusting These Brokers
Trump\s tariffs: How could they affect the UK and your money
Trump gambles it all on global tariffs he\s wanted for decades
TradingView Brings Live Market Charts to Telegram Users with New Mini App
Trump tariffs: How will India navigate a world on the brink of a trade war?
Interactive Brokers Launches Forecast Contracts in Canada for Market Predictions
Authorities Alert: MAS Impersonation Scam Hits Singapore
Stocks fall again as Trump tariff jitters continue
IG Group Acquires Freetrade for £160M to Expand UK Investment Market
Currency Calculator







