简体中文
繁體中文
English
Pусский
日本語
ภาษาไทย
Tiếng Việt
Bahasa Indonesia
Español
हिन्दी
Filippiiniläinen
Français
Deutsch
Português
Türkçe
한국어
العربية
GBP Forecast Q2 2022: The Bank of England's Inflation and Growth Puzzle
Abstract:4.4% in January. And even higher levels of inflation are expected in Q2 this year.
The Bank of England (BoE) is expected to raise UK interest rates further in the second quarter of 2022 as the UK central bank tries to stem soaring prices pressures. The BoE has already lifted the Bank Rate to 0.75% from 0.1% in late 2021 and money markets are currently pricing in 125 basis points of additional rate hikes this year. The latest Office for National Statistics (ONS) inflation release showed headline inflation hitting 6.2% in February, a fresh 30-year high, while core inflation rose to 5.2% from 4.4% in January. And even higher levels of inflation are expected in Q2 this year. The latest BoE monetary policy release shows that the UK central bank expect headline inflation to top 8% in the coming months, citing sky high energy and food prices as the main drivers of the move.
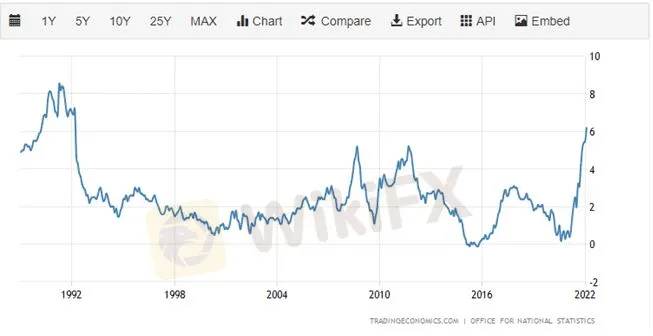
Source: TradingEconomic.com
The UK central bank recently pushed back against these market expectations, fearing that a series of hikes may stall growth in the months ahead. UK growth is now back above pre-covid levels and looks robust, despite fears that the Ukraine crisis, and Russian sanctions, will cause further supply chain disruptions. The latest BoE monetary policy report noted that while business confidence and labour market activity have remained robust, ‘consumer confidence has, however, fallen in response to the squeeze on real household disposable incomes’. It is this worry that a downturn in consumer spending will slow economic activity in the months ahead, especially with inflation expected to hit, and stay at, multi-decade highs. According to the BoE, UK GDP is now expected to be flat for Q1, compared to 1.1% in Q4 2021. The chart below shows that the central banks inflation expectations from the February MPC meeting are already on the low side.

Source: ONS and Bank Calculations
It is this inflation vs. growth conundrum that will cause Governor Bailey and the members of the Monetary Policy Committee to be flexible and yet still resolute in trying to quell inflation. If the central bank moves too hard, too quickly and causes growth to falter then fears of stagflation will hit the UK markets and Sterling. On the other hand if the BoE reacts to slowly and multi-decade high inflation becomes entrenched, then they will have too act even more aggressively to get a grip on UK price pressures. The Bank of England will need to balanced, sure footed and clear with their communications over the next few months if they are to succeed.
THE BRITISH POUND IN THE MONTHS AHEAD
Sterling has had a mixed Q1 and the outlook for the second quarter of the year is expected to continue these trends. GBP/USD slipped lower during the first three months of the year as the US dollar priced in a series of interest rate hikes during 2022 and into next year, widening the rate differential between the two currencies. Sterling rallied against the Japanese Yen, primarily due to JPY weakness, while EUR/GBP traded sideways with a slight negative bias. The British Pound also fell against the Australian dollar, as the commodity rich country benefitted from sharply higher metal and mineral prices. These, overall trends are likely to continue unless there is a major shift in the macro outlook, namely the ongoing crisis in the Ukraine.
Disclaimer:
The views in this article only represent the author's personal views, and do not constitute investment advice on this platform. This platform does not guarantee the accuracy, completeness and timeliness of the information in the article, and will not be liable for any loss caused by the use of or reliance on the information in the article.
Read more

Why Fed Keeps Interest Rates Unchanged, How Does It Affect To Forex Market?
Fed keeps interest rates at 4.25%–4.50%, impacting forex market. Dollar may rise as tariffs loom. Explore why rates unchanged and forex effects.

Do Tariffs Refueling Inflation? Understanding the Connection
Investigate how tariffs impact inflation. Learn how trade barriers influence prices and the broader economic landscape.

Will Trump's Trade Policies Fuel Inflation? BlackRock Warns of Economic Risks
Bitcoin and crypto prices plummet as recession fears and inflation warnings shake markets. Experts warn of prolonged economic challenges ahead.

How Will Central Bank Digital Currencies Could Shape Everything?
Central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) could reshape financial stability, addressing inflation, banking risks, and monetary policy challenges.
WikiFX Broker
Latest News
The Withdrawal Trap: How Scam Brokers Lure Victims into Paying More
FCA to Investors: Think Twice Before Trusting These Brokers
Trump\s tariffs: How could they affect the UK and your money
Trump gambles it all on global tariffs he\s wanted for decades
TradingView Brings Live Market Charts to Telegram Users with New Mini App
Trump tariffs: How will India navigate a world on the brink of a trade war?
IG Group Acquires Freetrade for £160M to Expand UK Investment Market
U.S. March ISM Manufacturing PMI Released
Should You Beware of Forex Trading Gurus?
Exposed by SC: The Latest Investment Scams Targeting Malaysian Investors
Currency Calculator







