简体中文
繁體中文
English
Pусский
日本語
ภาษาไทย
Tiếng Việt
Bahasa Indonesia
Español
हिन्दी
Filippiiniläinen
Français
Deutsch
Português
Türkçe
한국어
العربية
Popular Trading Concepts: Smart Money Concept (SMC) And Harmonic Patterns
Abstract:If you've been around Forex forums or social media recently, you've probably heard of Smart Money Principles (SMC) and Harmonic trading concepts.

You may be asking what the two mean, how they affect our everyday trading, and if all the buzz is justified. We will expose you to the three trading principles known as Smart Money Concepts (SMC), Harmonics, and Power Money in this article so you can make an educated choice about whether or not to use this method in your trading.
What exactly is SMC (Smart Money Concepts)?
Traditional Forex concepts like supply and demand, price patterns, and support and resistance are used in SMC trading, but everything has a new name and is said in a different way.
SMC traders discuss concepts such as “liquidity grabs” and “mitigation blocks.” Even if their comments seem unusual, a closer look at SMC reveals that it is a more typical style of trading than it appears at first.
SMC is more than a Forex trading method; it is a concept about how markets function.
SMC basically claims that market makers (banks, hedge funds, etc.) are manipulative institutions that intentionally make life tough for ordinary traders.
SMC fundamental ideas and terminology
When you first learn about SMC, it seems incredibly technical. The simplest vocabulary may leave you scratching your head. To assist you, here are some definitions of terminology often used by SMC traders:
Order blocks are a kind of phrase used to explain supply and demand. Some SMC traders argue that order blocks are a more “refined” idea than standard supply and demand, while others disagree.
Support and resistance are referred to as “breaker blocks” and “mitigation blocks.”
The phrase “fair value gaps” refers to an imbalance. There are several sorts of gaps, all of which were recognized years ago. Common gaps, fatigue gaps, breakaway gaps, and runaway gaps are a few examples.
Once you find out what the sophisticated language is referring to, you'll realize that other SMC principles are also known to you.
When evaluating markets, SMC places a strong emphasis on “break of structure,” or “BOS.”

SMC's Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of SMC:
Some traders seem to benefit from smart money concept trading. There is no reason not to utilize it if it works for you. It is more vital to be able to continuously comprehend what the price is doing and benefit from its behavior than to understand why the price is moving the way it is.
Price action has a long history of providing outcomes for many individuals, not only in currencies but also in other assets. SMC has a strong core since it is repackaging pricing activity.
When price activity is shown as SMC, some individuals find it simpler to grasp.
While the argument that huge institutions are targeting retail traders is questionable, it does seem feasible that larger institutions may sometimes go after smaller ones, resulting in part of what we are witnessing. Even though SMC presents them in a dubious context, liquidity grabs definitely occur. So, some of SMC's theoretical pieces may be realistic, but not in the way SMC portrays them.
Disadvantages of SMC:
When you consider how insignificant retail traders are to the major players, several of the theoretical parts of SMC do not seem to make much sense. Believing everything SMC says might lead to a misunderstanding of market fundamentals.
One cannot confirm or reject the hypotheses behind SMC. They are totally hypothetical, and only an insider could provide real proof either way. That is, no one can prove that SMC's model of reality is true, but no one can completely deny it either. All anybody can do is debate about what organizations do depend on their beliefs.
Switching up all the terminology as SMC does might make studying price action needlessly complicated, particularly if you are already acquainted with the normal language of price action. It may also make sharing what you learn with those who speak the usual price action language more difficult.
Many people are put off by the elitist aura surrounding SMC and believe that selling old principles as though they are fresh is misleading. Also, the term “sell” is used extremely literally here. While there are many free SMC resources, learning SMC will expose you to several cost walls.
What exactly are Harmonic Patterns?
Harmonic patterns are trend reversal patterns that use Fibonacci extensions, retracement levels, and geometric structures to reverse a trend.
These patterns alert traders to the possible reversal zone, allowing them to enter reversal trades when the market is nearing exhaustion.
What do these patterns resemble?
In general, all harmonic patterns are built on five price turning points.
Each harmonic pattern, however, has a unique geometrical form and Fibonacci ratio. These are the points X, A, B, C, and D. Each harmonic pattern has its own set of principles, which we will go over in more depth later in the essay.

What is the significance of these patterns?
The primary function of harmonic patterns is to forecast price fluctuations.
Day traders may estimate the future movement of financial instruments such as stocks, options, and more by identifying patterns of varying magnitudes and durations and applying Fibonacci coefficients to them.
Harmonic patterns are essential for detecting reversals. They are a very accurate device that characterizes extremely particular price changes.
Harmonic Pattern Types
Although there are several varieties of harmonic patterns, only a handful have withstood the test of time due to their frequency of occurrence on price charts. In this part, we will go through each one and explain how they vary.
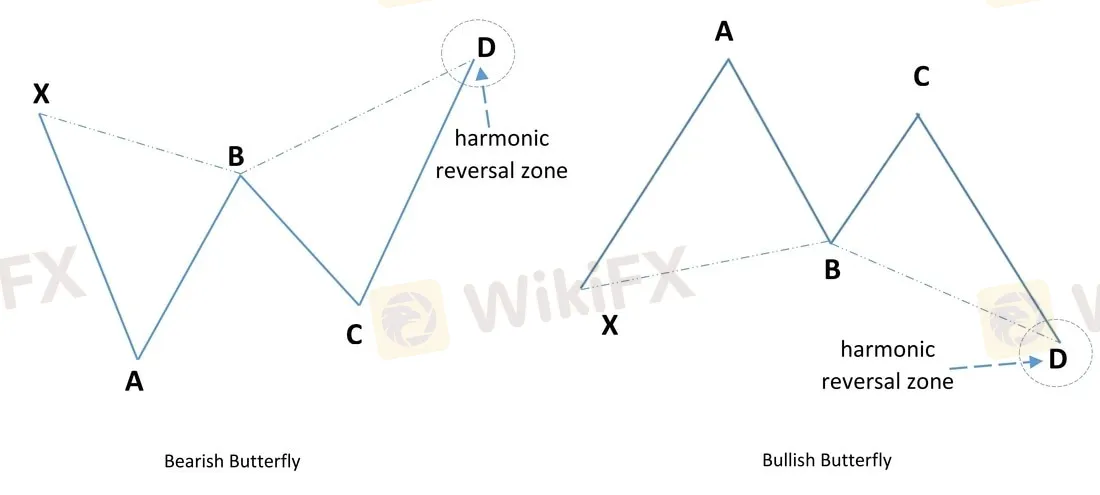
The Butterfly Pattern
The butterfly pattern is a kind of reversal pattern that appears towards the conclusion of a trend move. It was created by Bryce Gilmore and consists of five points: X, A, B, C, and D.
The pattern's qualities are as follows.
AB may retrace up to 78.6% of the XA leg. BC can retrace between 38.2% and 88.6% of AB. CD can be an extension of 1.618% - 2.618% of AB.
The Potential Reversal Zone is denoted by point D. (PRZ)
The Gartley Pattern
The Gartley pattern is a basic harmonic pattern that is preceded by a number that is either extremely low or very high. As previously stated, Harold McKinley Gartley created this design. It is also known as the '222' pattern, after the page number in his book Profits in the Stock Market on which it is described.


The pattern's criteria are as follows:
The AB leg should retrace about 61.8% of the leg XA.
BC is expected to retrace 38.2% - 88.6% XA.
Leg XA is at least 78.6% retraced in CD.
The Bat Pattern
Scott Carney discovered the Bat pattern in the early 2000s. The Bat pattern, like the Gartley pattern, is a retracement and continuation pattern. It occurs when a trend reverses direction momentarily but then returns to its previous route.

The following are the major rules of the bat pattern:
The AB leg may retrace between 38.2% and 50% of the XA leg.
The BC leg may retrace 38.2% to 88.6% of the AB leg.
The CD leg may retrace up to 88.6% of the XA leg's length.
CD leg may also be a 1.618% - 2.618% extension of the AB leg.
The Crab Pattern
This design was also devised by Scott Carney. He claims that is the finest harmonic pattern for trading. It's a reversal pattern with four legs labeled X-A, A-B, B-C, and C-D.
One big benefit of adopting the crab pattern over other kinds of harmonic patterns, according to Carney, is the high risk/reward ratio, which allows for extremely tight stop losses.
It gives traders the ability to join the market at extreme lows or highs.

Crab designs must adhere to the following guidelines:
The AB leg should retrace between 38.2% and 61.8% of the XA leg, whereas the BC leg should retrace between 38.2% and 88.6% of the AB leg.
C should never be more than point A's maximum (or low)
The longest leg is CD, which should stretch to 161.8% of XA. In extremely severe situations, the CD might extend between 224.0% and 361.8% of the BC leg.
The Cypher Pattern
The cypher pattern consists of five touchpoints separated by four waves, or legs. Each touchpoint indicates a reversal level, and each leg represents a price action.
It uses Fibonacci ratios that are tighter (often less than 1), which gives it a sharper look.


Rules for Cypher Patterns:
An impulse leg (XA) is followed by a retracement leg (AB) that achieves at least the 38.2% Fibonacci retracement of the XA leg without surpassing 61.8%.
If you trade this advanced harmonic price action pattern properly, you may get a high hit rate and a reasonable average reward-to-risk ratio.
The Shark Pattern
Another sort of harmonic pattern is the shark pattern. It is one of the most recent harmonic trading patterns used by traders since 2011.
The pattern is called a “dorsal fin” because its sharp outer lines and a small dip in the middle make a chart that looks like the back of a fish.


Harmonic Patterns in Trading
Harmonic Pattern trading is identical to trading any other chart pattern.
The following are the most important variables to consider:
Before using real money, practice trading these patterns on a simulator.
Before initiating a transaction, always set a profit and loss aim.
Determine the entrance and exit positions for each pattern.
Trade only A+ setups.
In conclusion
Every trader aspires to be a successful trader. It is not difficult to learn to trade the market by employing these two notions.
Always keep your stop losses and target levels at appropriate price levels in mind.
Stay tuned for more Forex news.
Download the WikiFX App from the App Store or Google Play Store to stay updated on the latest news.

Disclaimer:
The views in this article only represent the author's personal views, and do not constitute investment advice on this platform. This platform does not guarantee the accuracy, completeness and timeliness of the information in the article, and will not be liable for any loss caused by the use of or reliance on the information in the article.
Read more

President of Liberland Vít Jedlička Confirms Attendance at WikiEXPO Hong Kong 2025
Vít Jedlička, President and Founder of the Free Republic of Liberland, has confirmed his participation in WikiEXPO Hong Kong 2025, one of the most influential Fintech summits in the industry. The event will bring together global leaders, innovators, and policymakers to delve into the future convergence of technology and society.

Is Billion Bucks Fx Scam?
Recent claims on YouTube and social media platforms allege that Billion Bucks Fx is a scam broker. Many traders have reportedly lost money after investing with this broker, and it has been given a notably low score of 1.06/10 by independent rating platforms. In this article, we break down the details of Billion Bucks Fx, assess the risks, and provide insight into whether investors should be wary of its services.

SocialFi and the Forex Market: A New Era for Decentralized Social Trading?
The worlds of social media and decentralized finance (DeFi) have converged under a new banner—SocialFi. Short for “Social Finance,” SocialFi leverages blockchain technology to reward user engagement, giving individuals direct control over their data and interactions. While SocialFi has primarily emerged in the context of content creation and crypto communities, its principles could soon revolutionize the forex market by reshaping how traders share insights and monetize social influence.

Do This ONE Thing to Transform Your Trading Performance Forever
The story is all too familiar. You start trading with high hopes, make some quick profits, and feel like you've finally cracked the code. But then, just as fast as your gains came, they disappear. Your account balance dwindles, and soon you’re left wondering what went wrong. Worse still, fear and confusion creep in, making every new trade a stressful gamble rather than a calculated decision. If this cycle sounds familiar, you’re not alone.
WikiFX Broker
Latest News
Forex Market Outlook: Key Currency Pairs and Trading Strategies for March 24–28, 2025
Singapore Police Crack Down on Scams: $1.9M Seized, 25 Arrested
Gold Prices Swing Near Record Highs
XTB Opens New Dubai Office
The Growing Threat of Fake Emails and Phishing Scams
Africa Cybercrime Bust: Over 300 Arrested in Fraud Crackdown
Hong Kong Banks and Authorities Collaborate to Freeze Fraudulent Accounts Faster
SocialFi and the Forex Market: A New Era for Decentralized Social Trading?
Is Billion Bucks Fx Scam?
BaFin Halts USDe Token Issuance, Citing Serious Compliance Failures
Currency Calculator







