简体中文
繁體中文
English
Pусский
日本語
ภาษาไทย
Tiếng Việt
Bahasa Indonesia
Español
हिन्दी
Filippiiniläinen
Français
Deutsch
Português
Türkçe
한국어
العربية
Why Interest Rates Matter to Forex Traders
Abstract:The forex market revolves around interest rates! In other words, global interest rates govern the forex market. The interest rate on a currency is perhaps the most important element in influencing its perceived worth.
The forex market revolves around interest rates!
In other words, global interest rates govern the forex market.
The interest rate on a currency is perhaps the most important element in influencing its perceived worth.
So understanding how a country's central bank makes monetary policy decisions, such as interest rate decisions, is critical.
Price stability, or “inflation,” is one of the most important factors influencing a central bank's interest rate choice.
Inflation can be defined as a gradual rise in the cost of goods and services.
Inflation is the reason why, in the 1920s, a nickel for a soda pop cost a nickel, but now people pay twenty times as much for the same product.
Moderate inflation is often recognized as a result of economic expansion.
Too much inflation, on the other hand, may be harmful to an economy, which is why central banks keep a close eye on inflation-related economic indices like the CPI and PCE.
| COUNTRY | CENTRAL BANK |
| Australia | Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) |
| Canada | Bank of Canada (BOC) |
| European Union | European Central Bank (ECB) |
| Japan | Bank of Japan (BOJ) |
| New Zealand | Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ) |
| Switzerland | Swiss National Bank (SNB) |
| United Kingdom | Bank of England (BOE) |
| United States | Federal Reserve System (Fed) |
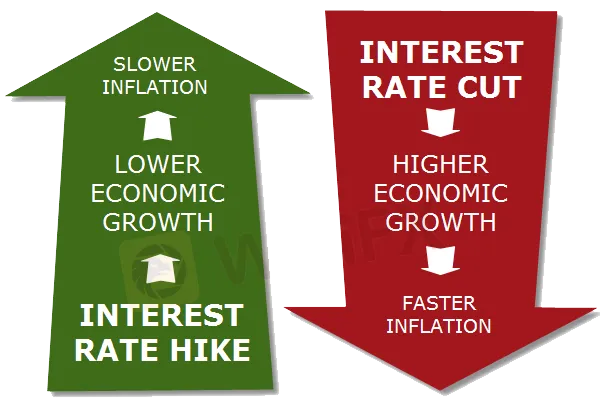
Central banks would most likely raise interest rates in order to control inflation at a manageable level, resulting in weaker overall economic growth and slower inflation.
This happens when high interest rates compel people and firms to borrow less and conserve more, stifling economic growth.
Loans are becoming more expensive, while cash is becoming more appealing.
When interest rates fall, however, individuals and companies are more likely to borrow (as banks loosen lending criteria), which boosts retail and capital expenditure and helps the economy thrive.
So, how does this relate to the FX market?
Interest rates determine the movement of global money into and out of a country, therefore currencies rely on them.
They're what investors use to decide whether or not to invest in a country.
Which would you select if you had the option to choose between a savings account with a 1% interest rate and one with a.25 percent interest rate?
You don't think so, do you?
Yes, we're tempted to do the same thing — store the cash beneath the mattress, if you get what we mean – but that's not an option.
Ha! Isn't it true that you'd choose the 1%?
We certainly hope so, since 1 is a multiple of 0.25 The same is true for currencies!
A country's currency is more likely to strengthen if its interest rate is greater. In the long run, currencies surrounded by lower interest rates are more likely to decline.
It's all really straightforward.
The major takeaway here is that local interest rates have a direct impact on how global market participants perceive a currency's worth in relation to another.
Interest Rate Expectations
Markets are always shifting in response to various events and conditions. Interest rates do the same thing — they fluctuate – but not nearly as frequently.
Because the economy has already “priced” current interest rates into the currency price, most forex traders don't spend much time thinking about them.
What matters more is where interest rates are expected to go in the future.
It's also worth noting that interest rates tend to fluctuate in response to monetary policy, or more precisely, at the conclusion of monetary cycles.
If rates have been falling for a long time, the reverse is almost certain to happen.
At some time, rates will have to rise.
And you can bet that speculators will try to predict when and by how much this will happen.
It's the nature of the beast; the economy will tell them. A shift in expectations signals the beginning of a shift in speculation, which will gain traction as the interest rate change approaches.
While interest rates fluctuate as the Federal Reserve adjusts its monetary policy, market sentiment can alter dramatically in response to a single report.
This causes interest rates to fluctuate more dramatically or even in the opposite direction than expected. So be on the lookout!
One of the most closely watched news releases is the one seen here, which is one of several ways to track interest rate forecasts.
The “dot plot” of the Federal Reserve.
The Fed Dot Plot, which is produced after each Fed meeting and illustrates the forecasts of the 16 members of the Federal Open Market Committee, is used by the US central bank to convey its expectation for interest rate course (the bigwigs in the Fed who are actually are in charge of setting interest rates).

Interest Rate Differentials
Pick a pair, any pair, and put them together.
Many forex traders utilise a method of comparing one currency's interest rate to the interest rate of another currency as a starting point for determining whether a currency will weaken or strengthen.
The “interest rate differential,” or the gap between the 2 interest rates, is the essential figure to watch.
This spread might help you see currency swings that aren't always clear.

An increasing interest rate disparity strengthens the higher-yielding currency, whilst a shrinking divergence benefits the lower-yielding currency.
When the interest rates of two nations move in different directions, some of the market's most dramatic swings occur.
The optimal equation for sharp swings is an increase in one currency's interest rate mixed with a reduction in the other currency's interest rate!
Nominal vs. Real Interest Rates
When individuals talk about interest rates, they are usually referring to either the nominal or real interest rate.
What's the difference between the two?
The nominal interest rate isn't necessarily indicative of the true situation. The nominal interest rate is the interest rate before inflation is taken into account.
Real interest rate = Nominal interest rate – Expected inflation
The stated or base rate is generally the nominal rate that you see (e.g., the yield on a bond).

Markets, on the other hand, are more concerned with the actual interest rate than with this rate.
If you possessed a bond with a nominal yield of 6% but inflation was 5% per year, the bond's true yield would be 1%.
That's a big difference, so keep that in mind when you're deciding between the two.
Disclaimer:
The views in this article only represent the author's personal views, and do not constitute investment advice on this platform. This platform does not guarantee the accuracy, completeness and timeliness of the information in the article, and will not be liable for any loss caused by the use of or reliance on the information in the article.
Read more

Forex is a game that I enjoy playing
These champions have one thing in common: they not only work their butts off, but they also enjoy what they do.

Wait patiently. Maintain your discipline
"Patience is the key to everything," American comic Arnold H. Glasgow once quipped. The chicken is gotten by hatching the egg rather than crushing it."

There isn't a Holy Grail to be found!
Ask any Wall Street quant (the highly nerdy math and physics PhDs who build complicated algorithmic trading techniques) why there isn't a "holy grail" indicator, approach, or system that generates revenues on a regular basis.

Concentrate on the Process. Profits aren't a priority
We've designed the School of WikiFX as simple and enjoyable as possible to help you learn and comprehend the fundamental tools and best practices used by forex traders all over the world, but keep in mind that a tool or strategy is only as good as the person who uses it.
WikiFX Broker
Currency Calculator






